


First-Order Grating G230MB
Description
The G230MB grating mode uses an intermediate resolution grating originally designed for use with the NUV-MAMA which has been redirected for use with the CCD to provide R~6000 spectroscopy in the near-UV which takes advantage of the CCD's higher throughput longward of 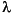 =2500 Å. The
=2500 Å. The G230MB grating mode has a spectral range from 1640-3190 Å.
As a single exposure with this grating covers only 150 Å, the grating must be scanned with a series of exposures taken at 11 distinct settings to cover the full spectral range of the grating.
Recommended Uses
The G230MB grating is designed for programs that require the highest available sensitivity in the near-UV from ~2500 to 3100Å or more generally to allow observations of sources too bright for the MAMAs in near-UV.
Special Considerations
In making the plots for the G230MB grating mode, we assumed that the CCD is subject to a change in the effective quantum yield resulting in the creation of multiple electron-hole pairs per photon for 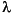 <3400 Å.
<3400 Å.
Also, because of the high sensitivity of the CCD to red light, observations of red stars with G230MB are more likely be affected by scatter than those using the MAMA G230M mode.
| Grating |
Spectral Range |
Average Dispersion (Å per Pixel) |
Plate Scale (arcsec / pixel) |
Tilts |
Central Wavelengths |
| Complete |
Per Tilt |
| G230MB |
1640-3190 |
155 |
0.15 |
0.05 |
Prime |
1713, 1854,1995,
2135, 2276, 2416,
2557, 2697, 2836,
2976, 3115 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Secondary |
2794 |
Figure 13.24: Wavelength Ranges for the G230MB Grating Settings
G230MB Sensitivities
Table 13.8: G230MB Throughputs & Sensitivities for a Point Source
| |
Sensitivity |
% Throughput |
| 1700 |
7.0E11 |
0.1 |
| 1800 |
1.8E12 |
0.3 |
| 1900 |
3.1E12 |
0.5 |
| 2000 |
4.6E12 |
0.7 |
| 2100 |
6.8E12 |
0.9 |
| 2200 |
9.5E12 |
1.3 |
| 2300 |
1.3E13 |
1.6 |
| 2400 |
1.4E13 |
1.7 |
| 2500 |
1.5E13 |
1.8 |
| 2600 |
1.5E13 |
1.7 |
| 2700 |
1.7E13 |
1.8 |
| 2800 |
1.9E13 |
2.0 |
| 2900 |
2.2E13 |
2.2 |
| 3000 |
2.7E13 |
2.6 |
| 3100 |
3.2E13 |
3.0 |
Figure 13.25: G230MB Point Source (left axis), and Diffuse Source (right axis) Sensitivities.
Note
Point source sensitivity assumes full transmission (zero slit losses). Diffuse source sensitivity assumes a 0.1" wide slit. To convert point source sensitivities to diffuse source sensitivities multiply the point source values by the grating spatial (cross dispersion) plate scale in units of arcseconds per pixel and by the width of the desired slit in units of arcseconds.
G230MB Signal-to-Noise
Note:
The top axis displays constant F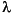 values corresponding to the STMAG units (V+STMAG
values corresponding to the STMAG units (V+STMAG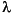 ) on the bottom axis. Recall that STMAG=0 is equivalent to F
) on the bottom axis. Recall that STMAG=0 is equivalent to F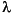 = 3.63E-9 erg cm-2 s-1 Å-1. The curves are labeled with exposure times in seconds.
= 3.63E-9 erg cm-2 s-1 Å-1. The curves are labeled with exposure times in seconds.
Figure 13.26: Diffuse Source Signal-to-Noise as a Function of STMAG for G230MB
Figure 13.27: Point Source Signal-to-Noise as a Function of STMAG for G230MB


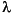 =2500 Å. The
=2500 Å. The 





